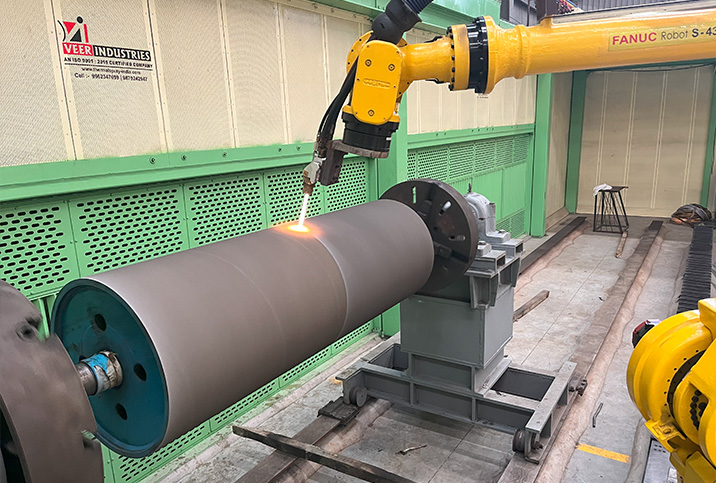
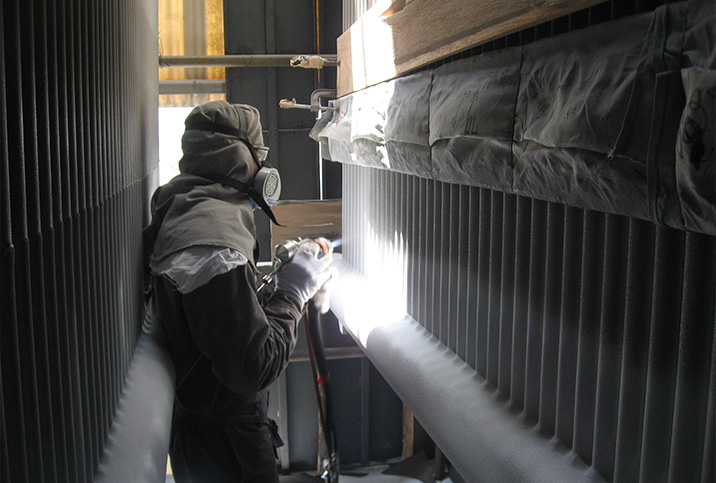
Thermal Spray Coating
Thermal spray processes can be used to apply engineering coatings’ to modify the surface properties of an item. Engineering coatings can provide such properties as enhanced wear resistance, thermal barriers, electrical / thermal conductivity, hard-chrome replacement and insulation across a wide range of applications.

Steel Industries
- Corrosion protection for steel structures, tools, and machinery exposed to harsh environments.
- Wear-resistant coatings for parts like rollers, dies, and furnace components.

Power Generation
- Turbine blades, rotors, and heat exchangers are coated with high-temperature-resistant alloys like Inconel or ceramic-based coatings to withstand extreme conditions.
- Boilers and gas turbines: Coatings that protect against erosion, oxidation, and thermal fatigue.

Pulp & Paper Industries
- Coatings for paper mill machinery (e.g., rollers, presses) to resist abrasion, corrosion, and wear.
- Protection for pumps, valves, and other processing equipment that come into contact with chemicals or high temperatures.

Printing Industries
- Coatings for printing rollers to prevent wear from contact with ink and paper.
- Protection of printing presses against corrosion and wear from chemical exposure.

Packaging & Corrugation
- Rollers, dies, and cutting tools are coated for wear and corrosion resistance.
- Machinery exposed to high friction and pressure during packaging processes is protected with wear-resistant coatings.

Glass Industries
- Coatings for molds and rollers used in glass production to prevent wear and reduce defects.
- Corrosion resistance for equipment exposed to high temperatures and chemical environments.

Chemical Industries
- Corrosion-resistant coatings for pipes, tanks, and reactors exposed to aggressive chemicals.
- Wear-resistant coatings for pumps, valves, and mixing equipment.

Oil & Gas Refineries
- Coatings for pipes, valves, and other equipment exposed to high pressure, heat, and corrosive substances in refineries.
- Protective coatings for drilling tools to reduce wear and corrosion.

Textile Industries
- Coatings for textile machinery parts, such as spindles and rollers, to improve wear resistance.
- Chemical resistance for machinery exposed to dyes and other chemicals.

Petroleum Industries
- Coatings for equipment in exploration, production, and refining processes to protect against corrosion and wear.
- High-temperature, high-pressure coatings for drilling tools and equipment used in harsh environments.
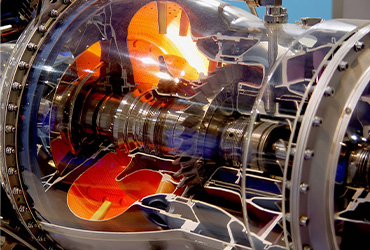
Aerospace Industries
- Turbine blades, engine components, and heat exchangers coated for high-temperature resistance.
- Wear-resistant coatings for landing gear, aircraft wheels, and other parts exposed to friction.

Cement Industries
- Coatings for cement plant equipment, such as rotary kilns, crushers, and grinding mills, to protect against wear and thermal damage.
- Corrosion-resistant coatings for machinery exposed to high temperatures and chemical environments.

Ceramic Industries
- Coatings for ceramic processing machinery to reduce wear and thermal fatigue.
- Protection of molds and tools used in ceramic manufacturing.

Energy Industries
- Coatings for equipment in power plants, including turbines, heat exchangers, and pumps, to protect against wear, erosion, and corrosion.
- Thermal spray coatings for energy storage systems, ensuring longevity and high efficiency.

Hydraulics Industries
- Coatings for hydraulic cylinders, pumps, and valves to protect against wear, corrosion, and cavitation.
- Protection for sealing surfaces exposed to high pressures.

Plastic Industries
- Coatings for plastic molding machines to reduce wear and improve mold release.
- Protection for tools and dies that come into contact with hot plastics and chemicals.

Military & Defence
- Coatings for military vehicles, weapons, and equipment to enhance durability and wear resistance.
- Corrosion-resistant coatings for naval vessels, tanks, and other defense infrastructure.

Marine Industries
- Coatings for ship hulls, propellers, and offshore structures to prevent corrosion from saltwater exposure.
- Anti-fouling coatings for underwater equipment to prevent marine growth.

Wind Energy
- Coatings for turbine blades to protect against erosion from wind, rain, and airborne debris.
- Corrosion-resistant coatings for offshore wind energy platforms.
Benefits
- Wear Resistance
- Corrosion Resistance
- High-Temperature Resistance
- Improved Durability
- Reduced Friction
- Rebuild surface area
- Cost-Effective Repair
- Versatility
- Electrical Insulation
- Customization
- Down-time Shutdown
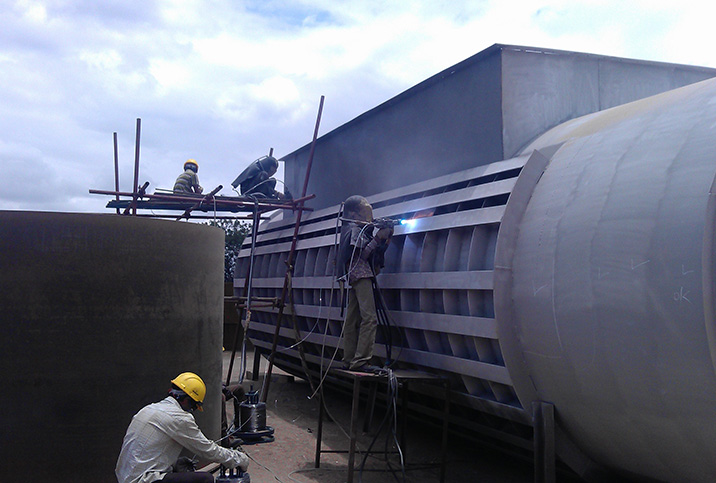
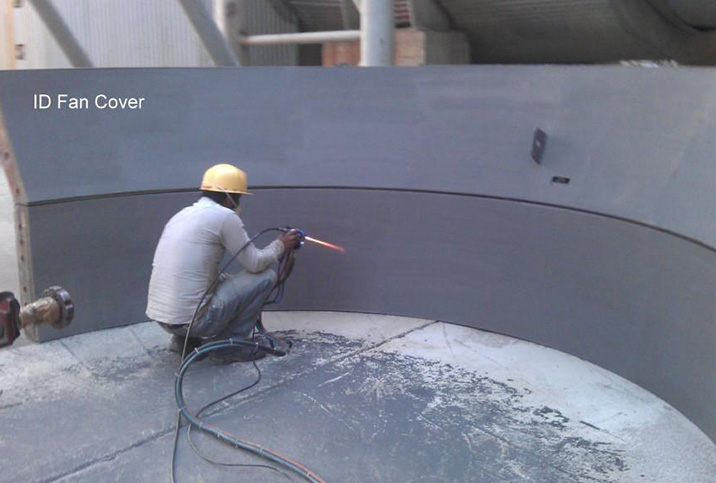
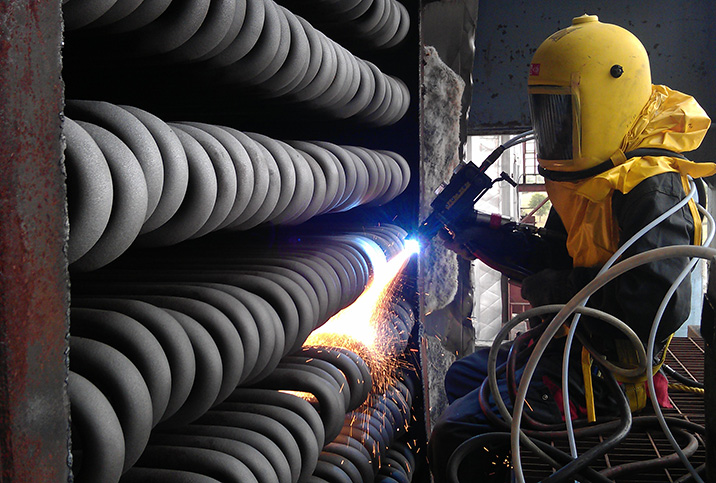





×
❮
![]()
